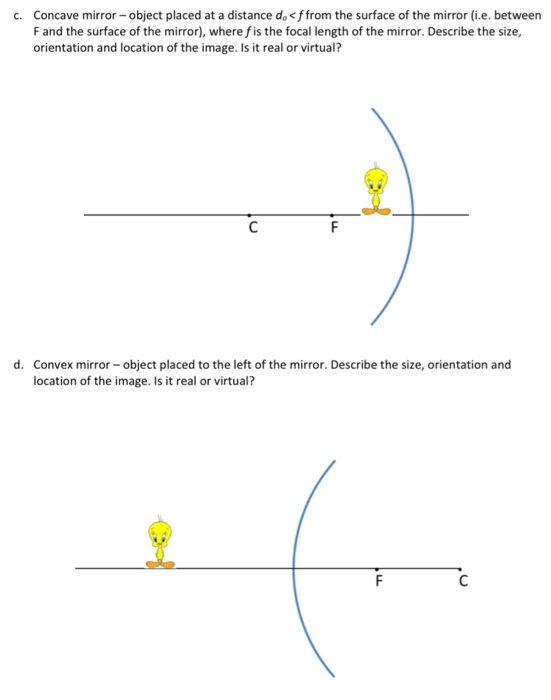
Describe the Three Principal Rays Used to Locate an Image
There are three principal rays. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection.
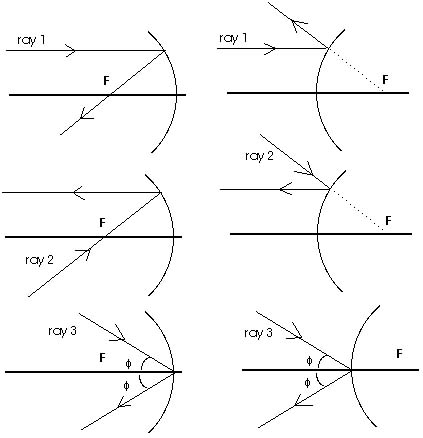
18 3 Images Formed By Curved Mirrors Prev Section Next Section Table Of Contents Chapter Contents In The Previous Section We Have Seen That An Object At Infinity Has An Image At The Focal Point After Reflection In A Curved Mirror Light Leaves The Mirror
Lets take an example of convex lens.

. So we will take an example of any lens. In fact we will usually ignore all the other rays and. It is useful to draw the third ray also to serve as a check on the other two.
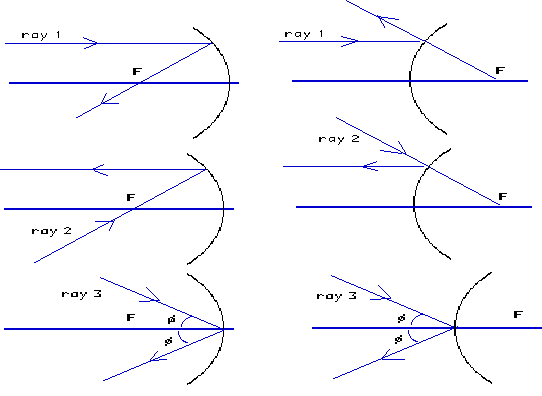
The 3 rays used to locate a lens image are the primary ray central ray and focal ray. For a concave mirror we see that ray passing through focus becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection For a convex mirror since focus is on the right side it appears that ray passes through focus and then it becomes parallel to principal axis Rule 3 - Ray passing through Center of Curvature will follow the same path back after reflection. Beyond the lens it will pass through the principal focal point.
Describe these three rays in terms of their orientation with respect to the principal axis and focal points. Jonathan is a published author and recently completed a book on physics and applied mathematics. Any ray passing or appearing to pass through the centre of Curvature is reflected along the same path.
State three rays that are usually used to locate images in curved mirrors by ray construction. Rays originating from the same point on the object are tracedthe three chosen rays each follow one of the rules for ray tracing so that their paths are easy to determine. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays.
Like so the first principle day which is used to determine the location of images the day which is parallel to the axis of the lens. When drawn properly your third ray does indeed pass through the location where the other two rays meet. List and describe the.
The second derivative or curvature of the graph at the principal-ray point is a measure of the tangential coma present in the lens. This is how an image is formed. In this case a real imageone that can be.
A ray drawn on a ray diagram that runs from the object to the lens parallel to the principal axis. Parallel to the principal axisthrough the focal pointthrough center of lens. While this image is formed by all the rays that leave the object and strike the mirror we will concentrate on three principal rays because they are easy to follow.
Ray diagrams are used to depict the image formation by tracing the path of light rays ie. Beyond the lens it will pass through the principal focal point. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye.
The three chosen rays each follow one of the rules for ray tracing so their paths are easy to determine. For each one below. Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in the figure.
Rays originating from the same point on the object are traced. So the question is we have to describe the three principal is which are used to locate the image of any source. Ray tracing is used to locate the image formed by a lens.
There are three convenient rays commonly used in ray diagrams to estimate the position of an image. Incident rays and reflected rays. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray.
If the ends of the portion of the graph used are above the principal ray this indicates positive coma. View the full answer. Any two of the three principal rays are sufficient to locate the image provided that you draw them correctly.
In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F the case of the object being located at 2F and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. Any ray that passes or appearing to be passing through principal focus is reflected parallel to the principal axis. 12 There are several properties of the lens you can change in this simulation.
The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. For a negative lens it w. In this case all four principal rays run along the optical axis reflect from the mirror and then run back along the optical axis.
How do they enter the lens and how do they exit the lens. All lenses and mirrors can use ray diagrams to find images. A graph that is horizontal at the principal-ray point indicates a flat tangential field.
For a convex lens the image will be upside down if the object is beyond f. Describe the three special principal rays. Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object.
Figure 1627 Ray tracing is used to locate the image formed by a lens. Take the pencil and raise it so that the craser is sitting on the principal axis. To completely locate the extended image we need to locate a second point in the image so that we know how the image is oriented.
1A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens. The ray passing through optical centre passes straight through the lens and remains undeviated. Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point.
They are drawn in order for anyone to view a point on the image of an object. These ray diagrams depend on the position of the object. You need to extend the ray backwards from the lens along the line that it.
In such cases a real image is formed. To draw a ray diagram. A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. 11 Draw the ray diagram.
The image is located at the point where the rays cross. The first principal ray occurs when the light comes in parallel to the principle axis it goes out through the focus. To do this we trace the principal rays from the base of the object.
A real image is an image that can be projected onto a screen. Click on the principal rays button. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer.
General rules for image formation using ray diagrams. A real image occurs when the light rays actually intersect while virtual images occur due to the apparent divergence of light rays from a point. A virtual image appears to come from behind the lens.
How many of the rays in questions 4 are necessary for. The three principal rays which are used for visualizing the image location and size are.
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

What Are The Three Principal Rays That Are Drawn To Construct The Ray Diagram For The Image Formed By A Lens Draw Diagrams To Support Your Answer

Images Formed By Convex Mirrors Ck 12 Foundation

3 Which Three Main Rays Are Used To Locate The Image Formed By A Spherical Lens Explain By Drawing Brainly In
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

Principal Ray An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
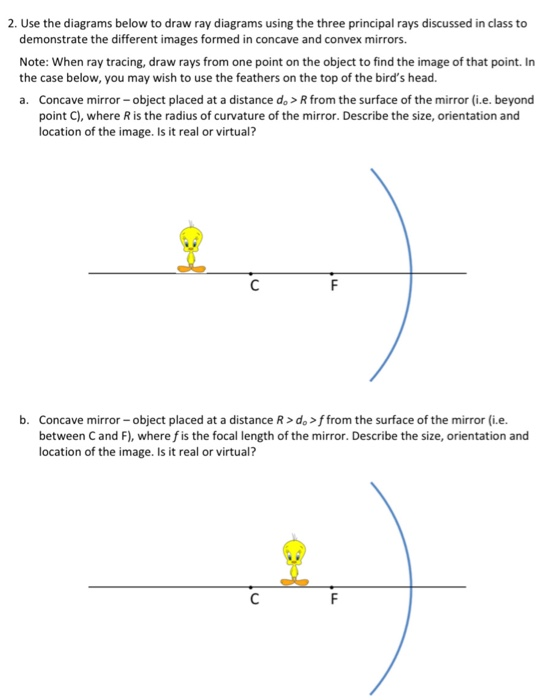
Solved 2 Use The Diagrams Below To Draw Ray Diagrams Using Chegg Com
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

Principal Ray An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Alberti S Window Perspective Has Been Used In Images Of The Renaissance And Is A Technology For Producing The Vi Virtual Reality Technology Virtual Technology
Physics Tutorial Ray Diagrams Concave Mirrors

Ray Diagrams Lenses Physics Lab Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
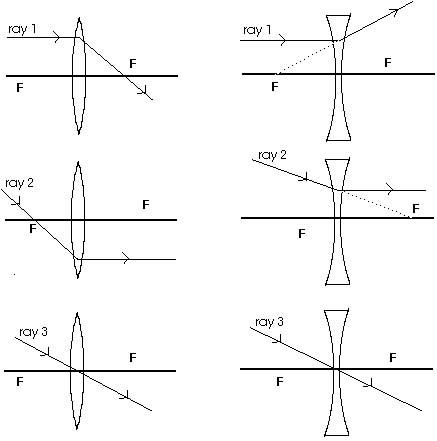
18 6 Images Formed By Lenses Prev Section Next Section Table Of Contents Chapter Contents As With Mirrors We Will Find It Extremely Useful To Look At Three Principal Rays Because It Is Easy To Predict Their Behavior They Are Sketched In Figure 18 16
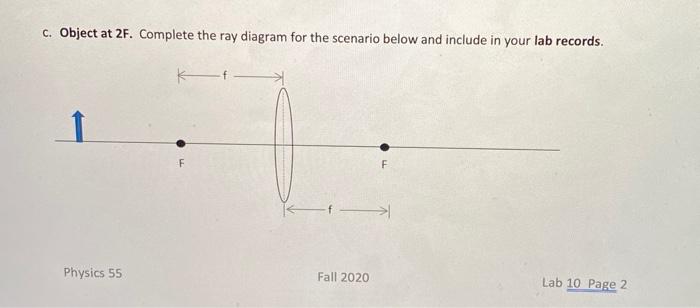
Solved 1 Converging Lenses The Pre Lab Notes Described How Chegg Com

3 Which Three Main Rays Are Used To Locate The Image Formed By A Spherical Lens Explain By Drawing Brainly In
Solved 2 Use The Diagrams Below To Draw Ray Diagrams Using Chegg Com

Comments
Post a Comment